Honored for balance of safety, convenience, infotainment
DETROIT – Connected World magazine awarded the Cadillac XTS a Connected Car of the Year award in the luxury category. Available in late spring 2012, the new XTS will debut Cadillac CUE, a comprehensive in-vehicle experience that merges intuitive design with auto industry-first controls and commands for information and media.
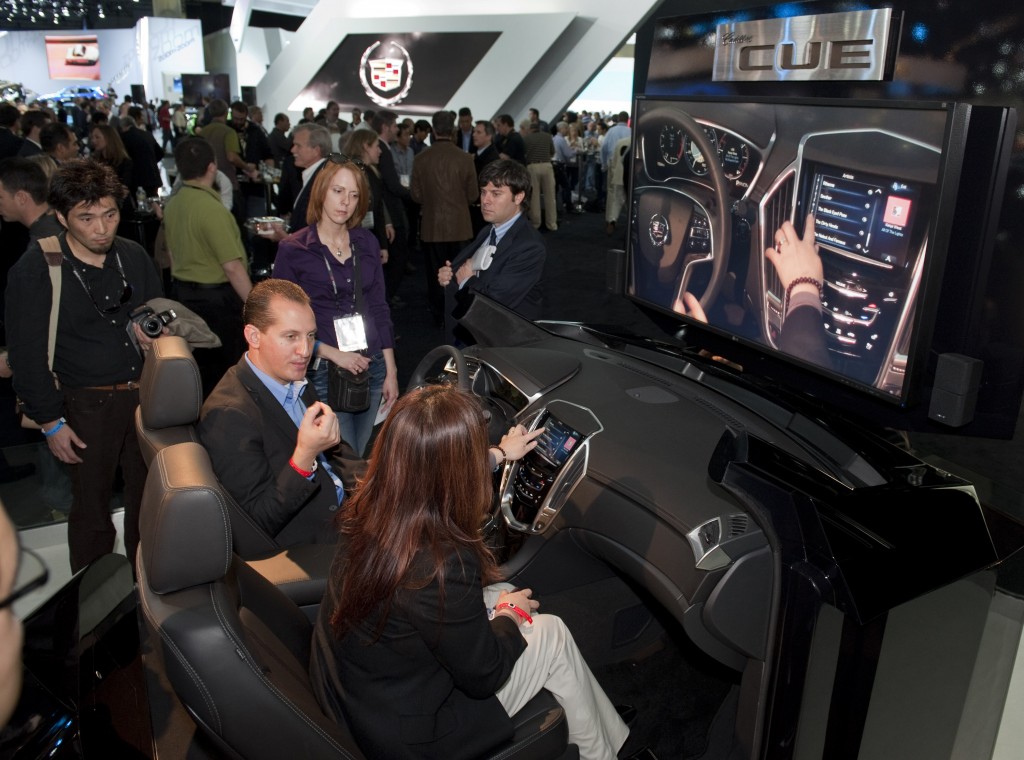

Cadillac CUE (Cadillac User Experience) Program Manager Jeff Massimilla (left) demonstrates the Cadillac CUE technology at the Los Angeles International Auto Show in Los Angeles, California. CUE is a full suite of infotainment, navigation and communication tools that combines natural voice recognition, fewer buttons, larger icons and greater customization to provide a more intuitive connected driving experience. CUE has 3.5 times more processing power than current auto industry systems. (Photo by Steve Fecht for Cadillac)
“Rather than just looking for power, speed, and performance, a connected car means turn-by-turn directions, voice-activated controls, and precollision systems,” says Peggy Smedley, editorial director, Connected World. “Car buyers now want it all under one hood and in the cabin.”
CUE, which stands for Cadillac User Experience, is a highly customizable user interfaces including a standard eight-inch (203 mm) screen in the “center stack.” CUE features several auto industry firsts, including capacitive-touch control with proximity sensing, gesture recognition and natural voice recognition.
The intuitive touch interface used in CUE is the same technology employed by many of today’s most popular handheld phones and tablets. Designed for both tech savvy and tech averse users, it allows consumers to securely store those mobile devices while channeling the information on those devices, along with navigation tools, weather maps with Doppler radar and AM/FM and XM radio.
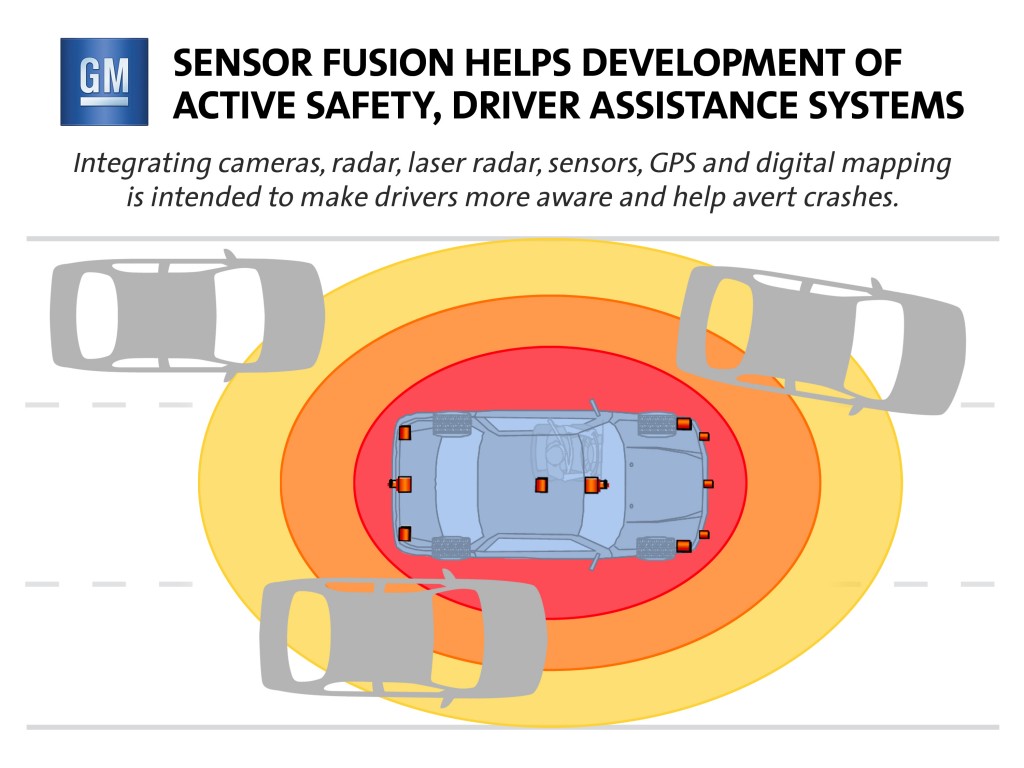
In addition to CUE, the XTS will debut a network of safety cameras, radar and ultrasonic sensors to bolster driver vision and awareness of road hazards and intervene to help avert potential crashes. In some cases, Cadillac’s enhanced vision and sensing systems will act without the driver, such as though automatic braking based on information indicating potential obstacles.
The Connected Car of the Year awards honor vehicles with technology that strike the right balance of safety, convenience, and infotainment. Chosen by the editorial team at Connected World magazine, the 2012 winners were named in small, mid-size, luxury, and ultra-luxury categorie